Diesel engines with turbocharging can significantly drain the driver's wallet. Let's explore the most popular BMW diesel engines, their technical specifications, labeling, and descriptions.
General Characteristics of BMW Diesel Engines
Compared to gasoline engines, diesel engines no longer feature the Valvetronic system and the well-known VANOS valve timing system. The latter system was only used in the most powerful variations of the six-cylinder N57.
The only system we also find is with triple turbocharging. Overall, BMW diesel engines have a single valve system, sometimes double, making turbochargers one of the most perishable components, as well as Common Rail injectors.
In some cases (for example, in the popular N47), you should pay attention to the service life, but the manufacturer constantly upgrades its devices to eliminate these defects.
Designations of BMW Engines
At the beginning, there is always a letter — M and N refer to standard engines in passenger cars, S denotes a special engine, for example, from M3, M5. The next two digits are used to indicate the number of cylinders. They are distributed as follows:
- 40-47 = four-cylinder BMW diesel engines,
- 50 and above = six-cylinder,
- 60 and above = eight-cylinder,
- 70 and above = twelve-cylinder engines
Only the 10-cylinder S85 and 4-cylinder N13, N20, and N26 violate this rule. After determining the number of cylinders, we find the type of fuel source (B — gasoline, D — diesel), displacement (20–2 liters, 30–3 liters, etc.)
And a code related to the design, informing, among other things, about factory changes (for example, TU — Technische Uberarbeitung, i.e. technical modification / revised version). An example of labeling: M57D30TU — diesel 3.0, type M57, after upgrade.
Most Common BMW Diesel Engines
Four-Cylinder Engines
M47
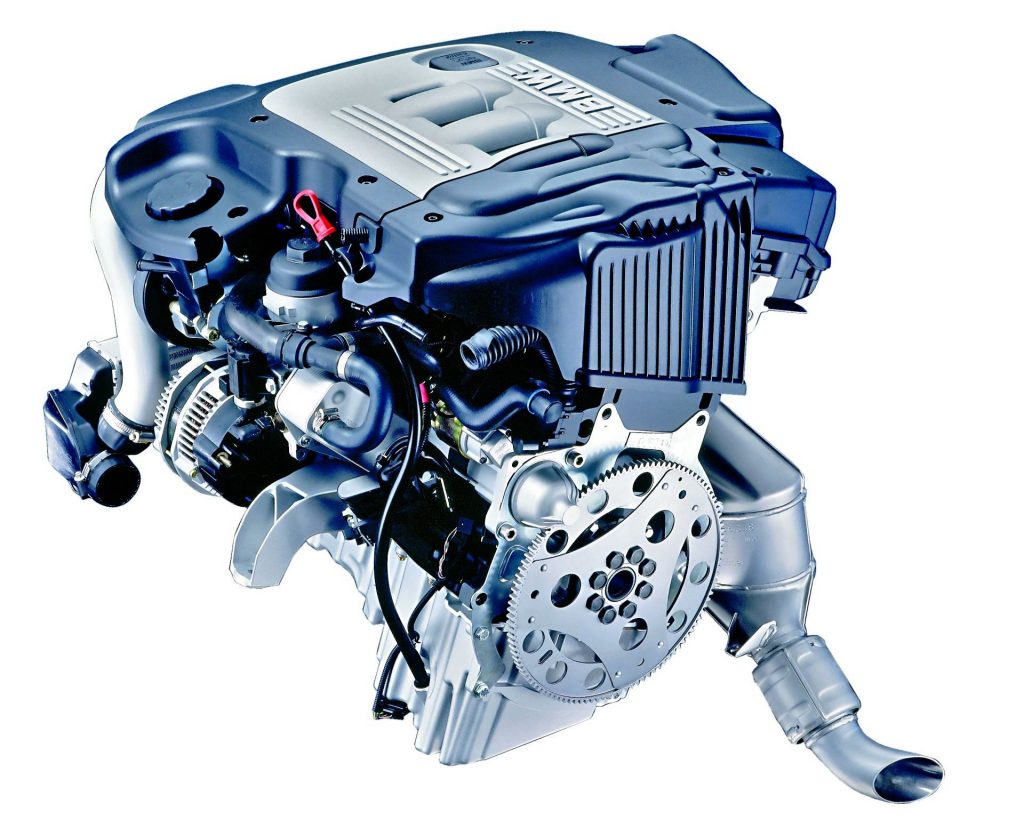
BMW M47
- turbo or bi-turbo engine, power 1.9-2.0
- direct fuel injection
- no VANOS system
- no Valvetronic system
Application: 1 Series (E87), 3 Series (E46, E90 — up to 2007), 5 Series (E39, E60 — up to 2007), X3 (X83 — up to 2007), Rover 75, Land Rover Freelander, MG ZT
This is the most common BMW engine on the market. Produced in 1998, it received a Common Rail fuel system after 3 years. Mostly found in models such as the E36 and E90, as well as in Land Rovers.
Due to its popularity, its drawbacks are well known. Primarily, throttle valves in the intake manifold tend to come loose over time. The injector is not durable, and too long oil change intervals lead to premature turbocharger failures.
N47
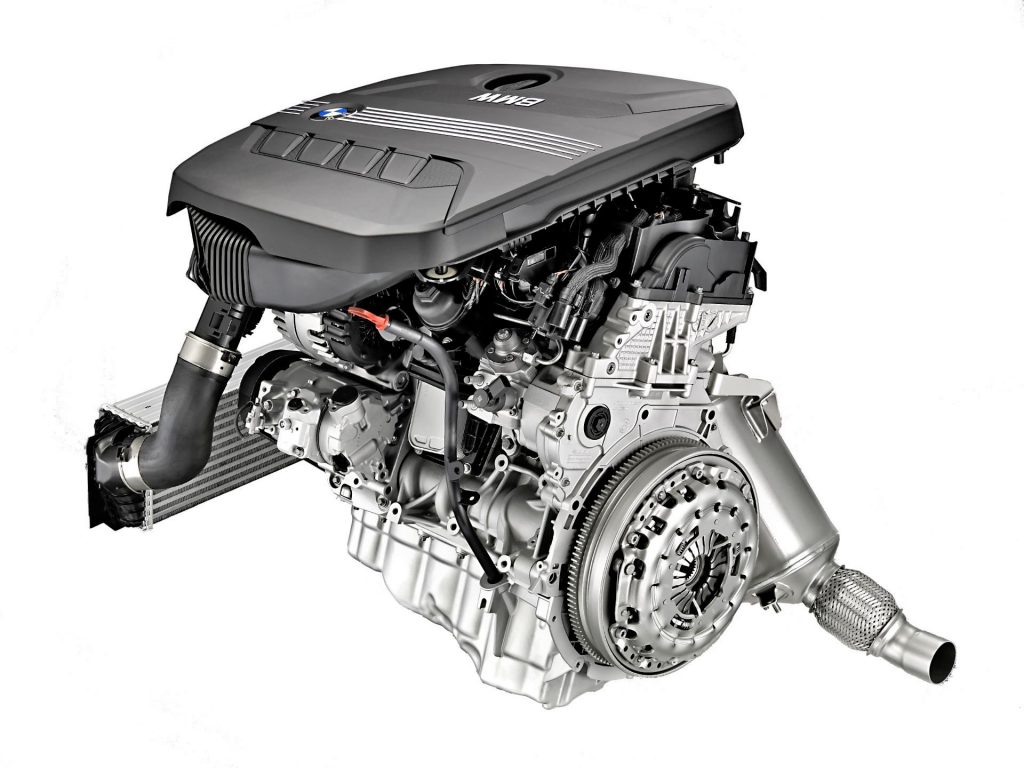

- turbo or bi-turbo engine, power 1.6-2.0
- direct fuel injection with Common Rail system
- no VANOS system
- no Valvetronic system
Application: 1 Series (E87, F20), 2 Series (F22), 3 Series (E90, F30), 5 Series (E60, F10), X1 (E84), X3 (E83, F25), X5 (F15), Toyota Avensis, RAV4, Verso
The new engine (introduced in 2007) is considered less problematic, although it spent time in the garage with many drivers due to its breakdowns. This was particularly evident with the timing belt, and due to its rear engine placement, the replacement cost a pretty penny.
In severe cases, a gear was even made, just integrated here with the crankshaft. The manufacturer addressed this issue as efficiently as possible (two upgrades, action to replace the upper chain tensioner), and this led to the expected result, significantly reducing breakdowns.
Six-Cylinder Engines
M57
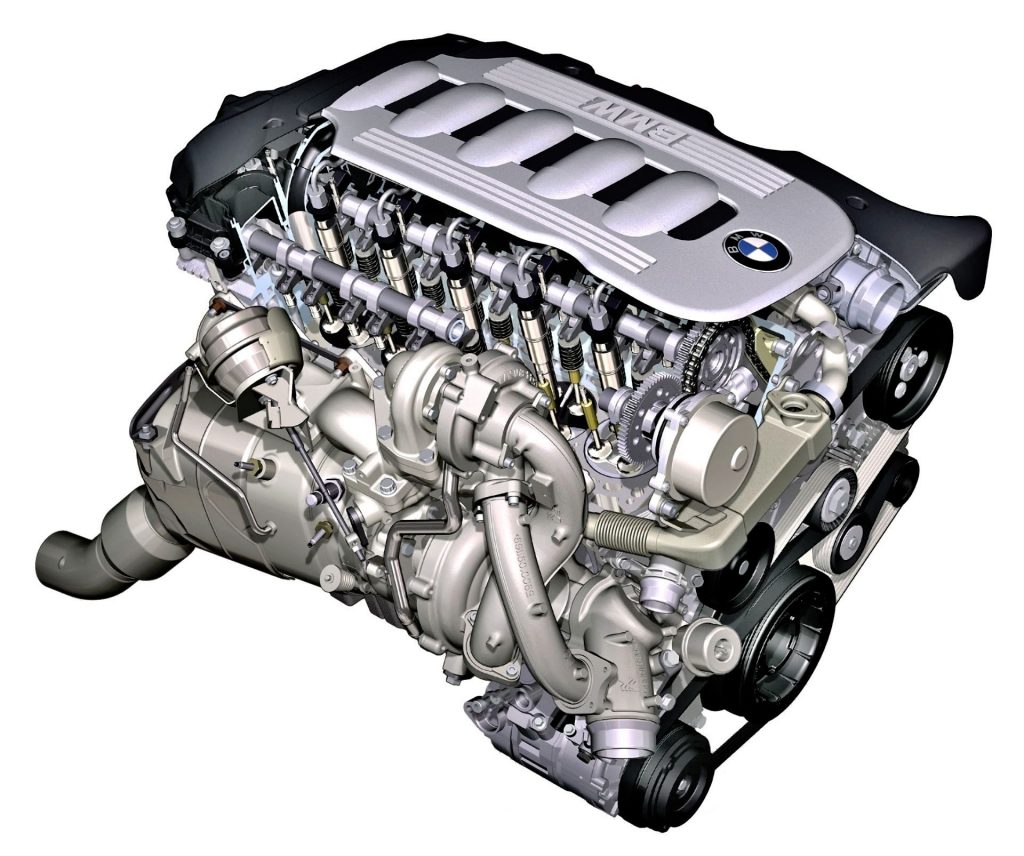

- turbo or bi-turbo engine, power 2.5-3.0
- direct fuel injection with CR system
- no VANOS system
- no Valvetronic system
Application: 3 Series (E46, E90), 5 Series (E39, E60), 7 Series (E38, E65), X3 (E83), X5 (E53, E70), X6 (E71), Range Rover, Range Rover Sport, Opel Omega
Another indestructible diesel engine from the end of the last century — there are even cases of covering a million kilometers. The Common Rail injection manifold originally had a capacity of 2.9 liters (later 3.0), while the economical option (2.5) was offered in Opel Omega.
With modernization, the design of the dual camshaft system was changed — the chain drives the first shaft and the second gear. In the following years, a particulate filter was also added.
In the M57 engine (fortunately, only in the modernized version marked TU), the fuel injection manifold membranes, which develop play, most often fail. Additionally, the pulley disintegrates on the crankshaft, and injectors fail, but only after a mileage of over 500,000 km.
N57
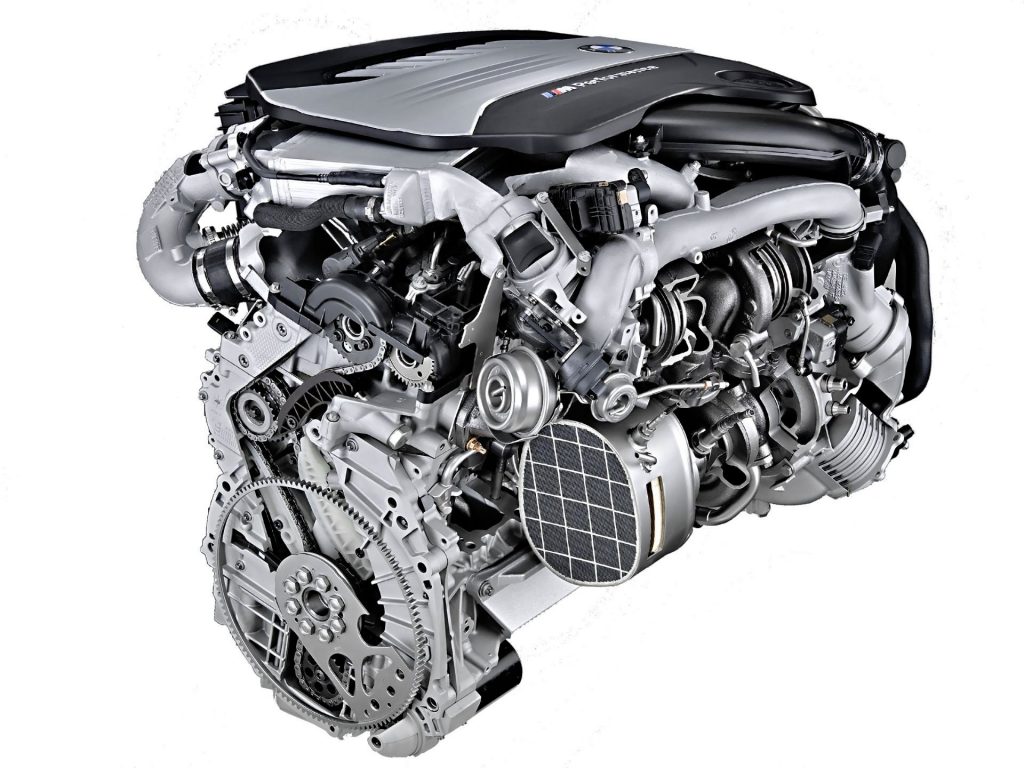

- turbo or bi-turbo engine, power 3.0
- direct fuel injection with CR system
- VANOS system in stronger versions
- no Valvetronic system
Application: 3 Series (E90, F30), 4 Series (F36), 5/5 GT Series (E60, F07 / F10), 7 Series (F01), X3 (F25), X5 (E70, F15), X6 (E70, F16)
The engine is entirely made of aluminum, as the only BMW diesel with the VANOS system. However, this only occurs in the bi-turbo version (300 hp) and the top variant with three turbochargers, generating a powerful 381 hp.
The N57 can only be found in combination with an automatic transmission, and it is considered a reliable engine and more stable than other BMW diesels. Due to the direct injection, the issue of soot in the intake channels is not a hindrance. However, the exhaust gas cooler is prone to damage, causing fluid leaks later on.
BMW 8-Cylinder Diesel Engines
M67
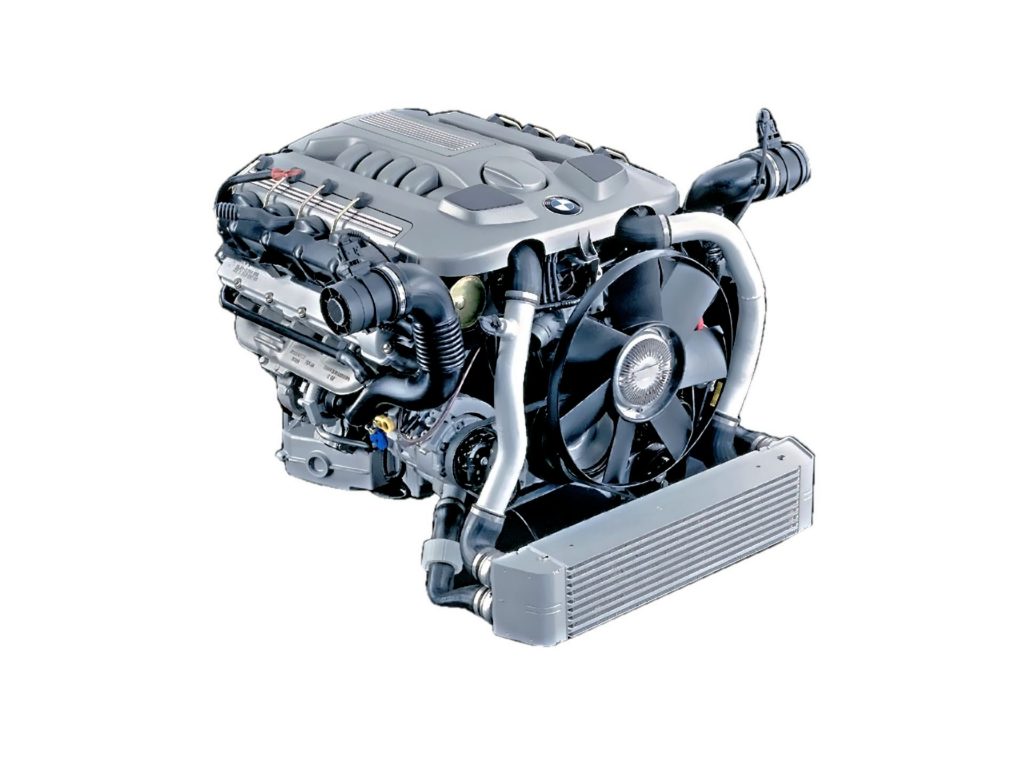

- bi-turbo engine, power 3.9-4.4
- direct fuel injection with CR system
- no VANOS system
- no Valvetronic system
Application: 7 Series (E38, E65 / 66)
A robust V8 engine used in two generations of the 7 Series (E38, E65). It consumes very little, around 15 l / 100 km, but it will go half a million kilometers before the first repair. The only thing you need to do is restore the injectors and turbocharger.
BMW Diesel Engine Table
| Двигатель | Расположение цилиндров | Объем | Максимальная мощность | Крутящий момент |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M47 | ||||
| M47D20 | R4 (турбо) | 1951 см3 | 116-136 л.с. | 265-280 Нм |
| M47D20R | R4 (турбо) | 1951 см3 | 116-136 л.с. | 265-280 Нм |
| M47TUD20 | R4 (турбо) | 1995 см3 | 122-163 л.с. | 280-340 Нм |
| Двигатель | Расположение цилиндров | Объем | Максимальная мощность | Крутящий момент |
| M57 | ||||
| M57D25 | R6 (турбо) | 2497 см3 | 163 л.с. | 350 Нм |
| M57TUD25 | R6 (турбо) | 2497 см3 | 177 л.с. | 400 Нм |
| M57D30 | R6 (турбо) | 2926 см3 | 184-193 л.с. | 390-410 Нм |
| M57TUD30 | R6 (турбо) | 2993 см3 | 204-266 л.с. | 410-560 Нм |
| M57TU2D30 | R6 (турбо) | 2993 см3 | 197-286 л.с. | 400-580 Нм |
| Двигатель | Расположение цилиндров | Объем | Максимальная мощность | Крутящий момент |
| N47 | ||||
| N47D16 | R4 (турбо) | 1598 см3 | 95-116 л.с. | 235-260 Нм |
| N47D20 | R4 (турбо) | 1995 см3 | 116-184 л.с. | 260-380 Нм |
| N47D20 | R4 (битурбо) | 1995 см3 | 201-218 л.с. | 400-450 Нм |
| Двигатель | Расположение цилиндров | Объем | Максимальная мощность | Крутящий момент |
| N57 | ||||
| N57D30U0 | R6 (турбо) | 2993 см2 | 204 л.с. | 450 Нм |
| N57D3000 | R6 (турбо) | 2993 см3 | 245 л.с. | 500 Нм |
| N57D3001 | R6 (турбо) | 2993 см3 | 258 л.с. | 560 Нм |
| N57D30T0 | R6 (битурбо) | 2993 см3 | 306 л.с. | 600 Нм |
| N57D30T1 | R6 (битурбо) | 2993 см3 | 313 л.с. | 630 Нм |
| N57S | R6 (битурбо) | 2993 см3 | 381 л.с. | 740 Нм |
| Двигатель | Расположение цилиндров | Объем | Максимальная мощность | Крутящий момент |
| M67 | ||||
| M67D40 | V8 (битурбо) | 3901 см3 | 234-241 л.с. | 560 Нм |
| M67TUD40 | V8 (битурбо) | 3901 см3 | 254 л.с. | 600 Нм |
| M67D44 | V8 (битурбо) | 4423 см3 | 299-329 л.с. | 700-750 Нм |




